
try .. catch... finally
1. 기본 frame
try{
내가 실행할 코드
}catch(e){ // e 또는 err 또는 error 아무거나 변수명으로 입력!
코드에 에러가 발생되면 여기에 실행할 코드 (error handling)
}1. 설명
1. try { ... } 의 코드 실행
-> 에러가 없다면 try 만 실행하고 catch는 건너 뛴다.
-> 에러가 있다면 ->
2. try{ ... } 코드 실행이 중단되고 catch{ ... } 로 제어 흐름이 넘어감. -> 에러가 나도 catch에서 에러 처리하기 때문에 스크립트는 죽지 않는다.
try 안의 코드를 실행, 예외(exception)이 발생(throw) 할 경우의 응답을 지정한다.
throw = 예외가 발생하는 경우 무엇을 할지 명시하는 코드를 포함한다.
1. try.. catch
2. try..finally
3. try..catch..finally
요렇게 3가지 방식으로 쓸 수 있다. try 중첩문도 가능하다.
2. * try.. catch 특징
오직 실행 가능한 Runnable 코드에서만 동작한다. 괄호 실수 등 문법적으로 잘못된 경우 tyr..catch가 동작하지 않는다. 이처럼 유효한 코드에서 발생하는 에러만 처리할 수 있다. 이러한 에러는 Runtime error, 런타임 에러 or Exception, 예외라고 부른다.
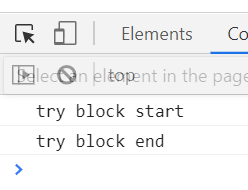
try { } 에 오류가 없는 경우
try{
console.log('try block start');
console.log('try block end');
}catch(e){
console.log('error');
}
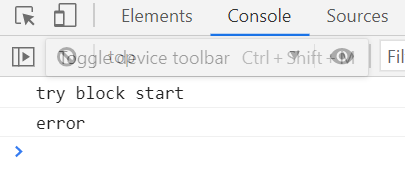
try { } 안에 오류가 있는 경우 - 정의되지않은 변수 만들어주기
try{
console.log('try block start');
hihi;
console.log('try block end');
}catch(e){
console.log('error');
}
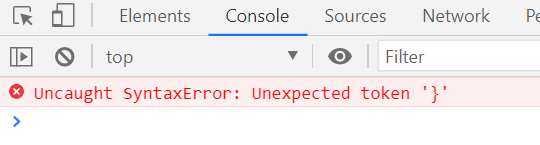
실행 불가능한 에러 경우
try{
console.log('try block start');
hihi;
console.log('try block end');
}catch(e){
console.log('error');
}}}}
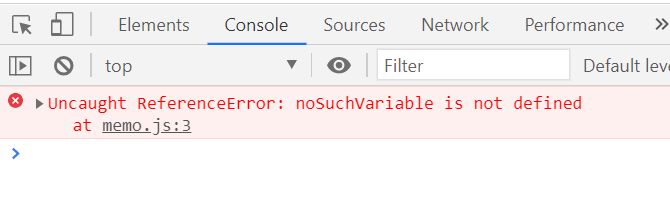
3. setTimeout처럼 scheduled 된 코드에서 발생한 예외는 try..catch에서 잡아 낼 수 없다.
(예외처리 경우만. try 안의 구문에 에러가 없으면 상관 없음)
try{
setTimeout(function(){
noSuchVariable;
},1000)
}catch(e){
console.log('error났다');
}
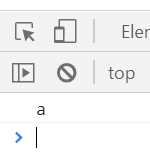
try 안에 오류가 없다면 아래처럼 상관 없다.
try{
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('a');
},1000)
}catch(e){
console.log('error났다');
}
try..catch 와 setTimeout 과 같은 scheduled 구문을 함께 쓰고 싶을 땐
setTimeout(function(){
try{
noSuchVariable;
}catch(e){
console.log('error났다');
}},1000)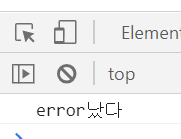
setTimeout 함수를 try...catch 전체를 감싸주면 된다.
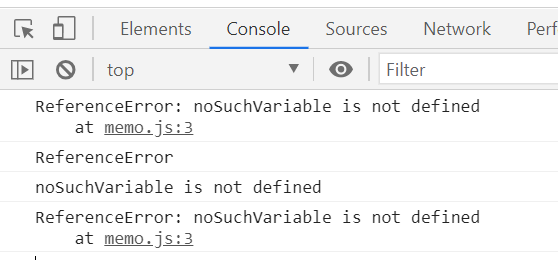
4. 에러가 나면 JS는 에러 상세 내용이 담긴 객체를 생성 -> catch 블록에 이 객체를 인수 전달함.
try{
noSuchVariable; 정의되지 않은 변수; - 고의로 에러 내기
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
console.log(e.name);
console.log(e.message);
console.log(e.stack);
}
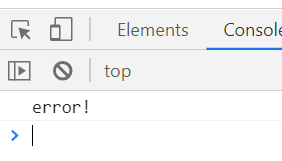
5. catch 뒤에 (e) 는 생략 가능 (최신버젼)
try{
noSuchVariable;
}catch{
console.log('error!')
}
----------------------------------------------------------try catch 실습 ------------------------------------------------------
처음 try...catch...finally를 접했을 때 어려웠는데 아래의 실습 (?) 연습을 해보았더니 이제 이해가 된다.
아래 코드들을 직접 타이핑하고 결과값을 확인하면서 익혀보기를 추천!
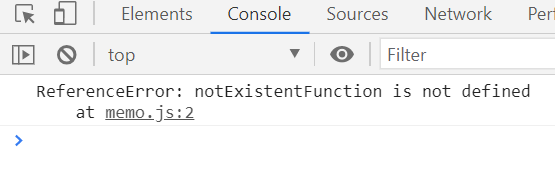
try{
notExistentFunction();
}catch(error){
console.log(error);
}notExistentFunction() 함수를 실행해라! -> 함수가 정의된 게 없음 -> error 를 catch 해서 {console.log(error)}를 실행 :
try{
let A = '안녀엉ㅇ'
console.log(A)
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}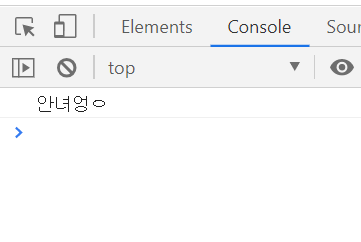
에러가 없어서 try 문만 실행됨
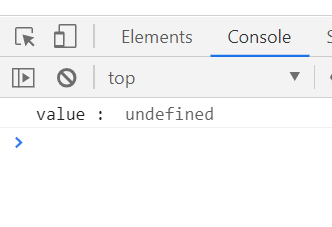
let req = undefined;
try{
if(req==undefined){
throw undefined;
}
}catch(e){
console.log('value : ', e);
}
req == undefined 라면 undefined 를 throw to e ?
throw
여기서 살짝 헷갈리는데 throw 가 뭔고 하니 throw [any Object] <- 요 부분을 catch (error) <- 여기로 넣어라 같다.
Throw! 던지고 Catch! 잡는 세트같음.
more examples ↓↓↓↓
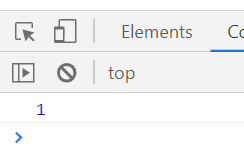
try{
throw 1;
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}
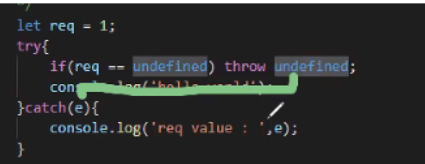
let req = 1;
try{
if(req==undefined){
throw undefined;
}
console.log('hello')
}catch(e){
console.log('value : ', e);
}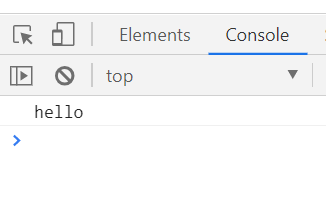
req는 undefined 가 아니므로 if 문을 pass, console.log('hello')를 찍음.
catch는 오류일 때라서 pass!
let req = 1;
try{
if(req==1){
throw undefined; // throw 가 실행되면 바로 catch! 로 가기
}
console.log('hello')
}catch(e){
console.log('value : ', e);
}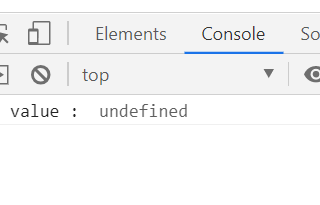
req==1 이라면 throw 해라 undefined를 to e로 그리고 try 구문에서 나가라! 라는 뜻으로 해석됨
--------------------------------------------함수 안에서 try...catch문 만들어 보기 ---------------------------------------------
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error"; // "error" 를 e 로 넣어라
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}
}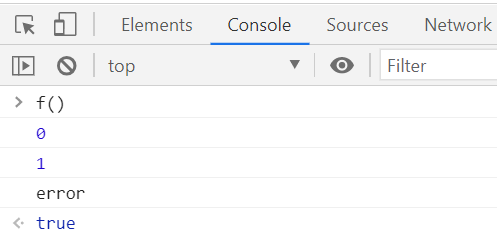
console.log에 f()를 입력해보면
결과값이 요렇게 나온다.
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error";
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return 3;
}
}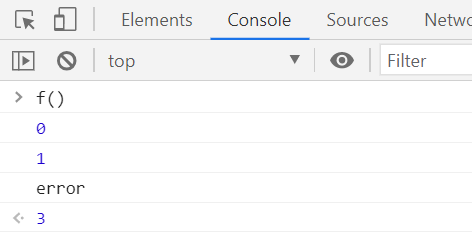
return 뒤 나오는 것을 출력
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error"; // throw 라는 구문 이 있으면 try 안 오류 없어도 error를
}catch(e){ // catch 구문의 인자값 e로 넣고 실행해 ! 라는 뜻
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}finally{
console.log('the end');
}
}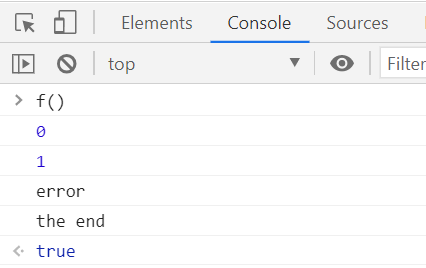
try 문에 오류가 없어도 throw 실행하면 catch 로 이어짐
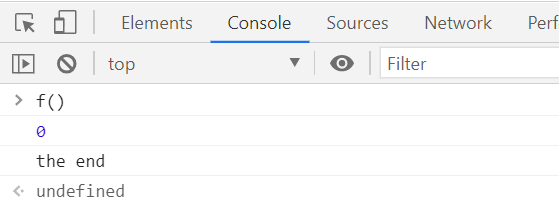
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
// throw "error"; try 안 에러가 없을 때 throw 도 없으면 catch구문 실행x
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}finally{
console.log('the end');
}
}
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error";
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}finally{
console.log('the end');
return false;
}
}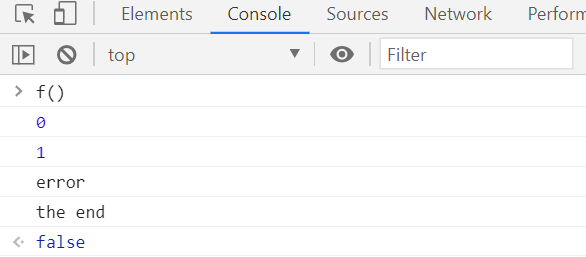
catch 끝에 return
finally 끝에 return
finally 마지막에 나온걸로 실행됨
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error";
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}finally{
console.log('the end');
}
}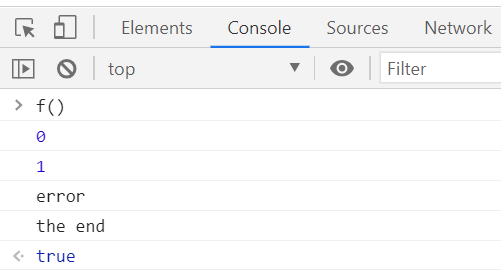
catch 안에 return 있는데
return 값이 가장 마지막에 나오는 걸 알 수 있다.
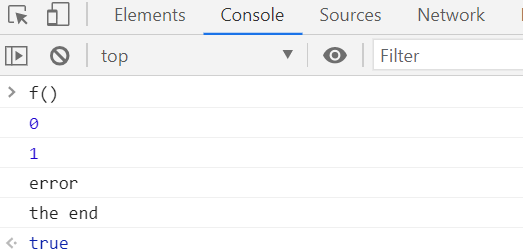
function f (){
try{
console.log(0);
throw "error";
console.log('나도 log해쥬!'); // logged 되지 않는다.
}catch(e){
console.log(1);
console.log(e);
return true;
}finally{
console.log('the end');
}
}-> throw 이후의 구문들 ( only in try문) 은 실행이 안되고 바로 catch로 간다.
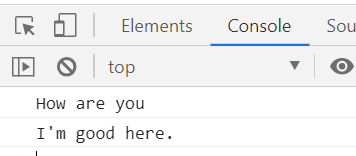
let req = undefined;
try{
console.log('How are you');
if(req==undefined) throw "I'm good here.";
console.log('How about you'); // throw 로 인해 제어가 catch로 넘어감
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}
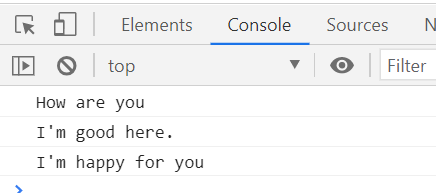
let req = undefined;
try{
console.log('How are you');
if(req==undefined) throw "I'm good here.";
console.log('How about you');
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}finally{
console.log("I'm happy for you")
}
let req = 1;
try{
console.log('How are you');
if(req==undefined) throw "I'm good here.";
console.log('not good');
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}finally{
console.log("I'm happy for you")
}
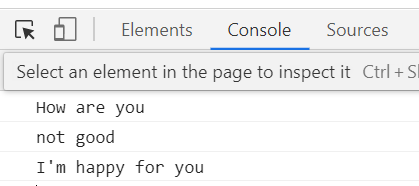
finally 는 결과값 상관없이 모두 실행됨!





